An artist's representation of what planet Gliese 832c might look like. Image via PHL @ UPR Arecibo
Gliese 832c, a planet about 16 light years away from Earth, has excited the scientists who found it, since Gliese 832c could potentially be one of the most Earth-like planets found to date.
The scientific team from New South Wales in Australia discovered the planet, which is also known as HD 204961 or LHS 3685, orbiting a red dwarf star about half the size of our own sun, according to Sci-News.com.
The red dwarf was first discovered in 2009, but this latest discovery of Gliese 832c could prove it’s the most similar planet to Earth because it would receive the same amount of energy from its own sun as we do from ours.
However, Gliese 832c has some differences from our own planet. Estimates place the planet at about 5.4 times the size of Earth, with an orbital period of 35.68 days.
This new discovery joins Gliese 667Cc and Kepler-62e as the most exciting examples of potentially habitable planets.
Prof Chris Tinney, a member of the team that discovered Gliese 832c, said that if life were possible on the planet’s surface, it would face some serious extremes in conditions.
“If the planet has a similar atmosphere to Earth it may be possible for life to survive, although seasonal shifts would be extreme.”
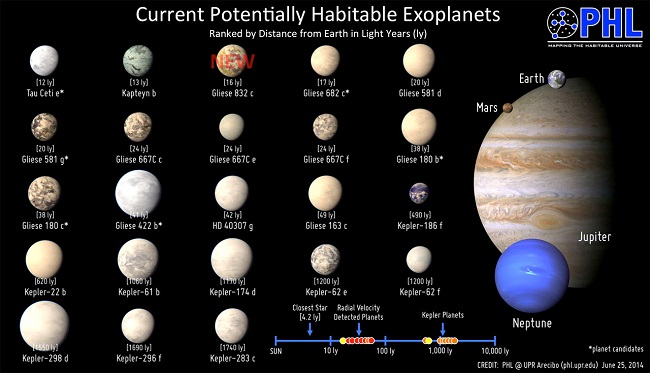
A size comparison with other potential life-harbouring exoplanets